Overview of the main Internet technologies. Possibilities of modern Internet technologies
Modern technologies make it possible to rationally organize a business in any area, manage various work processes remotely and carry out other work with minimal labor costs. Consider the most popular of them.
The World Wide Web is an unlimited space for collecting, processing and transmitting data of various formats.
With the help of innovative technologies, a person got the opportunity to communicate at a great distance, control a wide variety of production processes, and he can also minimize his labor to perform the most complex tasks, since this duty now lies entirely with special machines and programs that are installed on them.
Internet technology is a rapidly growing industry with incredible prospects.
The value and possibilities of Internet technologies for a person
The communication process between employees of companies or individuals is now taking place through the Internet. If earlier people used correspondence, telegraph and other methods of message transmission to communicate at a distance, today the vast majority of users prefer to communicate online.
Internet technologies and communications provide not only the transmission of voice and text messages, but also the transmission of information in any digital format.
The digital communication format provides:
- Instant data transfer in real time;
- Ability to transfer information in different formats;
- Ability to use different devices for receiving and transmitting data;
- Possibility to get remote access to data of enterprises, companies and industries.
These are far from all the opportunities and advantages that we received when the World Wide Web appeared.
Through the Internet, you can order and pay for various purchases and services, learn the most important news, find various information and exchange it with other users.
Despite the fact that millions of people use these services every day, the system has its own certain protection, which guarantees the confidentiality of personal information such as phone number, address and other data to each person.
Internet technologies increase business productivity
Internet technologies can be used not only for personal purposes, but also for successful business.
Modern networks help to significantly reduce human participation in any production processes, they contribute to the organization of a well-functioning structure.
Processing, receiving and transmitting data occur in a matter of minutes, so you can significantly reduce the cost of maintaining a staff of highly qualified professionals.
With the help of special software, personal computers and additional equipment, you can organize a complete and highly efficient workflow.
Also, with the help of innovative technologies, it is possible to automate the most complex production processes, thereby increasing productivity there.
Other Features of Internet Connection Technologies
Each user who wants to connect to the Internet must use the services of a provider - a company that provides access to the network and provides technical support to subscribers.
The technology for connecting to the Internet is different for each provider. Often, to establish a connection, a master comes to the site, he lays an Internet cable to your PC or to a router distributing Wi-Fi, connects to the server of his company.
Also, each subscriber has his own virtual personal account, in which he can check the status of the account and find out other useful information. The master gives the initial access code to the cabinet, this data is specified in the service agreement.
Internet connection technologies in smartphones and tablets are significantly different from connection technologies in PCs.
All mobile devices have a built-in Wi-Fi receiver, with which the gadget picks up a signal if it is within range. To connect to the network, you just need to press the appropriate button, which will give a command to the device.
You may also need to enter a special password that is used to protect personal networks. Computer networks and Internet technologies make it possible to be in touch almost anywhere, which is very convenient for users.
Users who use the mobile Internet from their mobile operator do not need to enter any additional codes or passwords at all in order to access the network. You just need to activate the mobile Internet and open the browser you need or the application.
Mobile Internet has the following advantages:
- Allows you to access the Internet almost anywhere;
- Does not limit users in mobility;
- Compatible with any mobile devices.
Internet technologies in the modern world
The Internet itself was created by the US military. It was originally designed to transmit data over secret channels, scientists managed to create a network whose components could function normally even if one of them was damaged.
Modern Internet technologies are the widest range of features and functions available to a wide range of consumers. The World Wide Web has found its application both in everyday life and in industries of various sizes.
Now not only people can connect to the Internet, but also various machines, household appliances and even entire systems.
Data transfer can be carried out in the following ways:
- Through twisted-pair telephone wires;
- By means of fiber optic cables;
- Via wireless systems such as satellites, cellular or radio relay.
Searching for information on the Internet as a convenient method of obtaining data
Modern technologies of information search on the Internet allow users to quickly find answers to any questions they are interested in.
In order to access the search engine website, you must have a browser installed on your PC, tablet or smartphone, and you also need to have an Internet connection.
After entering your request in the search bar, you need to click the "search" button, and the system will display all the articles and materials that have recently mentioned information of interest to you.
This method of obtaining data opens up the widest possibilities for users, information search technologies on the Internet help not only to find interesting news, goods in stores and nearby cafes, but also to engage in self-education.
Now young people can be trained remotely using the Internet, online courses are offered by the world's best universities.
Using Internet access technologies, you can significantly simplify all work processes, increase productivity and get many great opportunities.
Now all innovative inventions are somehow connected with the World Wide Web, which makes it possible to manage entire industries and enterprises in remote access mode, receive data in various formats, process them and transfer them in a matter of minutes.
Innovative Internet technologies at the exhibition
Central Exhibition Complex "Expocentre" offers to visit one of the the most important exhibitions of the year "Communication" which will be devoted to communications.
Participants will also be able to find new reliable partners and expand their customer base. Visitors will be very interested in the event, as it is possible to find reliable contractors and contractors, as well as order services from the world's leading companies.
You can register a ticket for the exhibition on the Expocentre website. To participate in the event, you need to fill out an application online or call.
Read our other articles:Internet technologies- these are communication, information and other technologies and services, based on which activities are carried out on the Internet or with the help of it. INFirst of all, these are, of course, sites, as well as: chat rooms, mail, online stores, forums, etc.
Since 1962, the US Department of Defense has been actively investing in the development of technologies for interaction between computers. Thanks to these studies, in 1969,The US military created a local area network - the predecessor of the Internet. Since 1972, our favorite e-mail has been functioning.
The 1990s became a turning point in the development of Internet technologies. With the invention of the first browser in 1993, the intended capabilities of the Internet began to take off.global character. Numerous telecom operators, e-commerce companies, software developers, and the like have emerged.
Nowadays, Internet technologies have found their application in all spheres of life of modern society and, first of all, of course, in the information sphere.
Logical components of Internet technologies
1) Internet services
* World Wide Web - World Wide Web
* Email. Teleconferencing systems
* File Transfer (FTP).
* Interactive chat (chat).
* Instant messaging (ICQ).
* Audio and Video conferencing.
2) Work on the Internet
* Browsers,
* Search engines. Internet navigation
* View a Web page in a browser.
3) Information resources on the Internet
* Web pages and Web sites, portals, Web space.
* Addressing, URL and data transfer protocols,
* Creation of Web pages. Web publishing languages.
* Publications on the Internet. Representation.
Provider– an organization providing Internet access services and other Internet-related services.
Services provided by an ISP may include:
- access to the Internet via dial-up and dedicated channels;
- allocation of disk space for storage and maintenance of sites (hosting);
- support for mailboxes or a virtual mail server;
- data backup and others.
Ways to connect to the Internet
The most common ways to connect to the Internet are:
1.Modem connection (dial-up access) - Dial-Up, ADSL
2. Leased line connection (optical fiber, etc.)
3.GPRS access (via cell phone)
4.Radio access
5.Satellite Internet
All of them differ from each other by the principle of operation, data transfer speed, reliability, complexity of equipment setup and, of course, price.
Transfer rate- this is the amount of information transmitted to the user per unit of time, usually measured in kilobytes / sec or kilobits / sec. For high speedchannels, the speed measurement is already in megabits or megabytes per second.
1. Modem connection (Dial-Up)- the oldest connection method, now it is popular only in cities where there is no wide choice of providers.
The advantages of such a connection are: ease of setup and installation of equipment (only an analog modem is required), low cost of equipment.
There are many more disadvantages of a modem connection: the subscriber's telephone line is busy, low data transfer rate, low quality of connection and data transfer due todeteriorating telephone lines.
At the speed provided by a modem connection, it is practically impossible to download large files from the Internet - videos, distributions of large programs, etc.
More promising than Dial-Up is currently the technology ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line). This is a technology that allows you to provideconventional analog telephone lines high-speed broadband Internet access. In addition, this technology does not load the subscriber's telephone line, thanks toseparation of signal ranges in a telephone line. The subscriber also does not need to call the provider. Cons - rather high cost of traffic.
2. Leased line connection
The provider conducts a leased line (twisted pair or fiber optic) to the subscriber's computer and issues a range of IP addresses for accessing the Internet. In this case, the user receivesfree telephone line, constant connection to the Internet, high quality connection and data transfer, high speed (up to 100 Mbps).
However, the cost of installing and configuring such a connection directly depends on the distance of the computer to the connection point of the provider, and in any case, it is quite highcompared to other connection methods. And when moving the computer to another place, you will again have to lay a cable to it.
Required Equipment
In this case, the user only needs a network card from the equipment, and at present it is available on almost any of the motherboards.
3. GPRS access
Almost all providers today offer the service of using a cell phone instead of a traditional modem. For the user, this connection to the Internet
The good news is that when the phone supports GPRS, all that is required from additional equipment is a device for connecting a mobile phone with a computer (USB cable, infrared port or
bluetooth). Another advantage is the mobility of this connection.
The data transfer rate depends on the mobile operator and the equipment used, but in general it is low - only twice as high as the modem one. Defining disadvantageis the high cost of traffic.
4. Radio access- a wireless way to connect to the Internet. The provider and the subscriber have all the necessary equipment (special radio modem, antenna), with
through which information is exchanged between the user and the Internet.
The disadvantages of radio access are the need to purchase expensive equipment and high subscription fees.
5. Satellite connection- it can be one-way (asynchronous) and two-way. The second, due to the high cost of equipment (the bill goes to tens of thousands), should not be considered we will.
Most often, satellite Internet is called an asynchronous (or combined) access method - data is received by the user through a satellite dish, and requests (traffic) fromof the user are transmitted by any other connection - GPRS or terrestrial channels (ADSL, dial-up). The main requirement for the request channel is the reliability of the connection. Mostcases, the best choice for him is an ADSL connection with free outgoing traffic.
Advantages satellite connection to the Internet - first of all, this is a very low cost of traffic - from 10 to 100 kopecks per 1 megabyte. The cost of a set of equipmentand connection is available to almost everyone and is approximately $200-300.
The data transfer speed varies greatly depending on the provider and the tariff plan chosen by the user. Satellite Internet providers offer verya wide range of tariff plans, including unlimited ones. A very nice bonus is also the possibility of free reception of satellite TV.
The disadvantage of a satellite Internet connection is the need for a channel for outgoing traffic - a telephone line or a telephone with GPRS support.
It is worth noting that in large cities of Russia, due to the growing competition of providers and the development of local networks, Internet access is becoming cheaper. You can often
set up unlimited access to the network with a decent speed and a monthly fee of 500-1000 rubles / month. In the provinces and small towns, this is much more difficult and prices are higher byorder. The best choice in this situation would be to use satellite Internet.
ADSL | TCP/IP | wifi | GPRS | DNS | FTP
Concept " Internet technologies"unites everything related to the Internet. These are all kinds of sites, chats, forums, e-mail, online commerce, online stores, social networks and much more that exists on the Internet or using the Internet. Internet technologies are subdivided according to certain criteria depending on the technical means (networks, servers, etc.) and special programs.
history internet technologies and the introduction of Internet technology into our lives, let's leave aside. Let's talk about where Internet technologies find their application and development.
What is internet technology? What is internet technology for?
First of all, modern Internet technologies allow you to create on the network:
Web servers;
- websites, portals and blogs;
- email;
- forums;
- chats and ICQ similar;
- videoconferences, webinars, teleconferences;
- wiki-encyclopedias.
Could we live without internet technology? Certainly. But modern Internet technologies bring humanity closer to the general availability of information or information resources and determine the further development of the whole society.
The number of Internet users is constantly growing, from curious freelancers to the Internet resources of government, public and social bodies. Therefore, it is difficult to do without new Internet technologies that automate the information resources of society, making them intuitively accessible and understandable.
Wireless WiFi and WiMAX also increase the number of Internet users. Now you no longer need to be “tied” to wired communication technology to access the Internet.
Internet technologies have made it possible to bring social communication of people to a new level. And this level and ways of communication are changing with the introduction of new Internet technologies.
Internet technologies are being actively introduced into the processes of education and retraining, and for all segments of the population from schoolchildren to the middle class. The introduction of Internet technologies in schools, institutes, online learning at home, seminars, webinars, web conferences is already becoming mandatory in any learning process.
Internet technologies force the development of Internet services. This is the security of the Internet, the engineering equipment of servers, data centers, sites of Internet providers.Everywhere already can not do without constantly developing Internet technologies.
Internet technologies are communication, information and other technologies and services that provide a business, information and entertainment environment on or through the Internet. Internet technologies are everything connected with the Internet.
The history of modern Internet technologies began in 1962, when the US Department of Defense actively invested in the development of technologies for interaction between computers. Thanks to these studies, in 1969, the local network was created - the predecessor of the Internet. Email has been around since 1972.
An important stage in the development of Internet technologies was the 90s with the invention of the first browser in 1993. Numerous telecom operators, e-commerce companies, software developers, and the like have emerged.
Today, Internet technologies find their application in all spheres of life of modern society and, first of all, in the information sphere.
Among the properties of Internet technologies that are of paramount importance for the development of modern society and the economy, six of the most important should be noted.
Internet technologies make it possible to activate the information resources of society, which today are the main factor in development.
Internet technologies allow optimizing (primarily automating) information processes. In many developed countries, the bulk of the working population is involved in the processing, storage and transmission of information products and services.
Internet technologies are used more and more every year in complex industrial and social processes.
Internet technologies create information interaction between people and are actively used in the preparation and dissemination of mass information.
Internet technologies have a tremendous impact on the intellectual development of society and the economy. In all countries, computer technology, educational programs and multimedia files are familiar attributes of everyday life.
Internet technologies play a key role in obtaining and accumulating new knowledge, the use of which increases the efficiency of economic processes.
These properties of Internet technologies provide the economies of all countries of the world with the opportunity to actively develop. At the same time, the introduction of Internet technologies in companies is not an easy process. This is due to the fact that Internet technologies are a complex system consisting of physical and logical components.

The physical components of Internet technologies include:
1) Internet network. TCP/IP protocols. IP addresses. The hierarchical system of Internet domain names. Internet backbone. Routing.
2) Software on the Internet. network operating systems. Special software for connecting to the Internet. Applied protocols.
3) Computers (servers and clients) on the Internet. Email servers. Web servers. FTP servers. teleconferencing servers. instant messaging servers.
4) Digital communication lines. Provider choice. Internet connection .
5) Internet access. Connecting the network card to the local network. Ethernet cable systems.
6) Remote access to global networks. Access "computer - network". Network-to-network access.
Physical components make it possible to make an assessment of the material values of Internet technologies, thanks to them the potential of new technologies on the Internet is realized.
The existence of the physical components of Internet technologies has given impetus to the development of the economies of individual companies, regions, and countries. In addition to the physical components of Internet technologies, there are logical components.
Logical components of Internet technologies:
1) Internet - services. World Wide Web - World Wide Web. Email. Teleconferencing systems. File transfer (FTP). Interactive chat (chat). Instant messaging (ICQ). Audio and video conferences. Voice communication (IP-telephony).
2) Work on the Internet. Browsers. Search engines . Internet navigation. Viewing a Web page in a browser.
3) Information resources on the Internet. Web pages and Web sites, portals. Web is space.
Examples of Internet technologies.
ADSL.

Bellcore is a pioneer in the xDSL family of Internet technologies.
Gnutella- a completely decentralized file-sharing network within the Internet, a descendant of Napster, is distinguished by the fundamental absence of a central server. A network is formed when one Gnutella user connects to another user.
POP3.
POP3- mail protocol. With it, we receive our mail from mail servers, for example, mail.ru. The corresponding service is launched on the server, and a client program is installed and configured on the user's computer - for example, The Bat!
IMAP.
IMAP ( Internet Message Access Protocol is an application layer protocol for accessing email. Similar to POP3, it is used to work with incoming letters.
SMTP.
SMTP used to send mail from users to servers and between servers for further forwarding to the recipient. The mail client must use the POP3 or IMAP protocols to receive mail.
gopher.
Protocol gopher Internet technology developed in 1991. Prior to the ubiquity of the World Wide Web (WWW) hypertext system, Gopher was used to extract information (mostly text) from a hierarchical file structure.
bittorrent.

bittorrent("bitstream") - a peer-to-peer (P2P) network protocol for cooperative file sharing over the Internet. With the help of this Internet technology, files are transferred in parts, each torrent client, receiving (downloading) these parts, at the same time gives (uploads) them to other clients, which reduces the load and dependence on each source client and provides data redundancy.
IRC.
IRC(Internet Relay Chat - relayed Internet chat) - a service system for communicating via the Internet in real time. This Internet technology is one of the means of real-time communication between Wikipedians.
dial-up.
Telephone communication via modem does not require any additional equipment. Since telephone points are available all over the world, this connection remains useful for travelers.
telnet.
telnet- Internet remote access technology that allows you to connect to another computer via the Internet. If the owner of another computer grants a remote user the right to connect to it, Telnet will allow commands to be entered to access programs and services on the remote computer.
usenet.
usenet(Uznet) - Internet technology used to communicate and publish files. Usenet consists of newsgroups to which users can post messages. Messages are stored on servers that exchange them with each other.
VoIP.
VoIP(Voice over IP; IP-telephony) - a communication system that provides the transmission of a voice signal over the Internet or over any other IP networks. The signal is transmitted digitally over the communication channel. In other words, VoIP VoIP is an Internet technology for transmitting voice information in real time over the Internet.
Skype.
Skype(Skype) - free closed-source software that provides encrypted voice communication over the Internet between computers (VoIP), as well as paid services for communication with subscribers of the conventional telephone network.
DNSSEC.
DNSSEC ( Domain Name System Security Extensions) - specification set, which ensures the security of information provided by DNS (Domain Name System) means of IP (Internet Protocol). This Internet technology has been used in Russia since the end of 2011, adds a digital signature to DNS queries.
wap.
WAP(Wireless Application Protocol) - "wireless access protocol" is an Internet technology for accessing Internet resources using only a mobile phone, without resorting to a computer and / or modem. In fact, it is a technical standard that describes the way in which information from the Internet is transmitted to the display of a mobile phone.
WAIS.
WAIS- network information retrieval system. This Internet technology uses the TCP/IP protocol to interface the client application with the information server. The client part has the ability to receive texts or multimedia documents stored on the server.
SSH.
SSH(Secure SHell - "safe shell") - Internet technology that allows remote control of the operating system. The protocol is similar in functionality to Telnet and rlogin, but at the same time, it encrypts all traffic, including transmitted passwords.
SSL.
SSL(Secure Sockets Layer - the level of secure sockets) - Internet technology that provides a secure connection between the client and the server. The SSL protocol was developed by Netscape Communications. Subsequently, based on the SSL 3.0 protocol, the RFC standard was developed and adopted, which received the name TLS.
TLS.
TLS(Transport Layer Security) is a cryptographic protocol that provides secure data transfer between nodes on the Internet. The TLS protocol is based on the Netscape SSL version 3.0 protocol and consists of two parts - TLS Record Protocol and TLS Handshake Protocol.
Internet radio.
Internet radio or web radio - a group of Internet technologies for transmitting streaming audio data over the Internet. The Internet uses both wired and wireless data transmission technologies, including satellite and cellular networks.
Wired terrestrial data transmission lines are WAN / LAN networks that use Ethernet technologies: VPN and a regular telephone line: DSL (ADSL), Dial Up.
Satellite Internet uses DVB technology, advantage: the choice of any satellite provider, such as SkyDSL.
Today, wireless data transfer technologies using Wi-Fi technology and the new WiMax data transfer protocol are spreading, followed by networks of cellular companies using GPRS and EDGE / 3G data transfer protocols.
Internet TV - IPTV.

Internet protocol television is an Internet technology that uses a two-way digital radio transmission signal based on IP video decoding and converting it into standard television signals.
Messengers - IMS.
Internet technology for instant messaging over the Internet in real time through instant messaging services (Instant Messaging Service, IMS). Text messages, sounds, images, videos can be sent, as well as activities such as drawing or playing together.
SPDY and ISDN.
SPDY is a web content transfer protocol from Google Corporation. The protocol is positioned as a replacement for the HTTP protocol.
Electronic payment systems.
WebMoney (for example) is the most popular email system. payments. Transfer of funds to an electronic wallet: bank transfer, replenishment through payment terminals, from a bank card, through other email systems. payments.
Examples of wireless Internet technologies by range:
1. Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPAN - Wireless Personal Area Networks). Technology examples - Bluetooth.
2. Wireless Local Area Networks (WLAN - Wireless Local Area Networks). Technology examples - WiFi.
3. City-wide wireless networks (WMAN - Wireless Metropolitan Area Networks). Technology examples - WiMAX.
4. Wireless wide area networks (WWAN - Wireless Wide Area Network). Technology examples - CSD, GPRS, EDGE, EV-DO, HSPA.
In this article, we have not touched on the "cloud" Internet technologies. But that's another topic for another article.
Internet technologies
As a result of studying the material in this chapter, the student should: know
- Internet technologies used in business;
- principles of use and examples of Internet search engines;
- concept, logic of work and types of virtual enterprises (VP);
- technology for building VP as a form of inter-industrial cooperation; be able to
- to use information technologies of the Internet in economic activity;
- build a model of the integrated information space of the EaP;
- create the organizational and functional structure of the EaP; own
- skills in using Internet technologies;
- technique of organizing flexible production structures based on Internet technologies.
Internet technologies used in business
Internet (English) Internet)- a worldwide system of interconnected computer networks for storing and transmitting information. She is also called World Wide Web And Global network, or simply Net. The World Wide Web and many other data transmission systems operate on the basis of the Internet.
WWW technology is an example of a universal global information storage, implemented within the limits of modern possibilities. This technology turned out to be very promising for the implementation of data exchange within corporate networks of enterprises.
The Internet consists of many thousands of corporate, scientific, government and home computer networks. The combination of networks of different architectures and topologies has become possible thanks to the Internet Protocol (IP). Internet protocol) and the principle of data packet routing.
From the point of view of terminology, there are two consonant terms - the Internet (internet) and the Internet (Internet). The term “Internet” refers to data exchange technologies based on the use of the TCP / IP protocol family, while the “Internet” is an association of world networks that use Internet technologies to enter, store, search and exchange data.
The history of the idea of the Internet is interpreted in different ways. It is known that the US Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency has proposed the creation of a computer network for defense purposes. The development of such a network was entrusted to the University of California at Los Angeles, the Stanford Research Center, the University of Utah and the University of California at Santa Barbara. The computer network was named ARPANET(English) Advanced Research Projects Agency Network), and in 1969, as part of the project, the network united the four indicated scientific institutions. All work was funded by the US Department of Defense. Then the ARPANET network began to actively grow and develop, it began to be used by scientists from different fields of science. The first ARPANET server was installed on September 2, 1969 at the University of California (Los Angeles). The Honeywell DP-516 computer had 24 KB of RAM. October 29, 1969 at 21:00 between the first two nodes of the ARPANET, located at a distance of 640 km - at the University of California Los Angeles (UCLA) and at the Stanford Research Institute (SRI) - held a communication session. Charlie Kline was trying to connect remotely from Los Angeles to a computer at Stanford. His colleague Bill Duvall from Stanford confirmed the successful transfer of each entered character by phone. The first time it was possible to send only two characters "LO" (originally it was supposed to send "LOG"), after which the network ceased to function. LOG should have been the word LOGIN (login command). The system was returned to working condition by 22:30, and the next attempt was successful. This date can be considered the birthday of the Internet.
However, there are currently studies, according to which it is recognized that the idea of V. M. Glushkov and one of the variants of the National Automated System (OGAS), developed in the 1960s. (see details in Chapter 9), is considered the prototype of the Internet system.
4. Internet search technologies
The main methods of searching on the Internet are hyperlinks, site names of directories and directories, search technology in Internet search engines.
Hyperlink for the user - a graphic image, video or text on a website, in an e-mail or in any electronic document that establishes a link and allows you to navigate to other objects on the Internet.
|
a brief description of |
||
|
In HTML documents, text links are highlighted in blue or underlined. When you hover over them with the mouse cursor in the browser window, you go to documents located on a local disk or on a computer network, or to elements of this object. When navigating the browser using the keyboard, text and graphic links are highlighted with a rectangular dotted frame |
||
|
Catalogs and reference books |
The directories have hierarchical thematic headings that indicate to a person how to move in the directory |
|
|
search engines |
They are based on searching by keywords and displaying the addresses of all pages on which these words occur. Popular search engines in Russia - Yandex, Google, Search.Mail.ru, Bing, Rambler, Yahoo! |
|
|
5. Technologies for transferring large amounts of information. Sound and video files |
These files have a large information volume. Transferring such files over computer networks in standard formats requires high-bandwidth communication lines. To reduce the volume of audio and video files without loss of quality, special file compression methods are used, based on the removal of audio or video information that is not perceived by a person. |
|
Web browsing is carried out with the help of special programs - browsers. Currently, the most common browsers are Internet Explorer, Mozilla, Safari, Opera and Google Chrome.
The browser window contains the standard application window elements:
- a window menu containing a set of commands "File", "Edit", "View", "Favorites", "Tools" and "Help";
- toolbar, the buttons of which allow you to switch from one web page to another (buttons "Forward", "Back", "Home"), as well as control the process of loading them (buttons "Stop", "Refresh");
- text field "Address", in which the Internet address of the desired web page is entered from the keyboard or selected from the list;
- the workspace in which web pages are viewed.
Currently, there are a fairly large number of services on the Internet that provide work with the entire spectrum of resources. The most famous among them are:
- DNS service, or domain name system, which provides the ability to use mnemonic names instead of numerical addresses for addressing network nodes;
- electronic mail (e-mail), which provides the possibility of exchanging messages of one person with one or more subscribers;
- an IRC service designed to support real-time text communication (chat);
- teleconferences, or newsgroups (Usenet), providing the possibility of collective messaging;
- FTP service (file transfer protocol - file transfer protocol) - a file archive system that provides storage and transfer of files of various types;
- Telnet service designed to manage remote computers in terminal mode;
- WWW - hypertext (hypermedia) system designed to integrate various network resources into a single information space;
- streaming media.
The listed services are standard. This means that the principles of building client and server software, as well as interaction protocols, are formulated in the form of international standards, and software developers are required to comply with general technical requirements during practical implementation.
Along with standard services, there are also non-standard ones, which are the original development of a particular company. As an example, we can cite various systems like Instant Messenger (a kind of Internet pagers - ICQ, AOl, Demos on-line, etc.), Internet telephony systems, radio and video broadcasts, etc. An important feature of such systems is the lack of international standards, which can lead to technical conflicts with other similar services.
Consider the main areas of use of Internet technologies.
- 1. Electronic business. According to research results, most of the Internet resources are somehow connected with commercial activities. The Internet is used for advertising and the direct sale of goods and services, for market research, electronic payments and bank account management, electronic commerce for goods and services, and digital products and services.
- 2. Mass media- online publications; news sites, literary, popular science, children's, etc. If offline publications are released periodically (once a day, week, month), then online publications are updated as new material appears. Internet radio and Internet TV also exist.
- 3. Literature, music, cinema. Electronic libraries accessible via the Internet contain a huge number of works. At the same time, many books available on the net have long become a bibliographic rarity, and some have not been published at all.
- 4. Connection- e-mail, IP-telephony, Skype, etc. The development of the Internet, used as a means of communication, leads to an increasing spread of such a form of employment as remote work.
- 5. Communication. The Internet is a way of mass communication of people united by various interests. For this, Internet forums, blogs and social networks are used.
- 6. Crowdsourcing. The Internet turned out to be a good tool for solving socially significant problems with the help of many volunteers coordinating their activities. One of the largest projects of this kind is Wikipedia, an online encyclopedia created by volunteers. Examples of so-called citizen science programs are Stardust@Home and NASA-sponsored Clickworkers, the Galaxy Zoo galaxy classification project; distributed computing projects such as Folding@Home, World Community Grid, Einstein@Home, and others can also be considered as citizen science, since the computations are carried out using volunteer computers.
- 7. Search for information. Provided by Internet search engines, examples of which are briefly described in the next paragraph.
A certain analogue of the Internet is intranet (intranet)- internal information network of the enterprise, built on the basis of Internet technologies. The benefits of these technologies include:
- ease of searching for information and navigation (by simply selecting a hypertext link, you can move from one network node to another);
- external attractiveness of the presentation of information (due to the use of WWW technology, textual information is supplemented by graphics, sound and other multimedia elements);
- the presence of a large number of useful services, such as news, e-mail, conferences, etc.;
- the possibility of free circulation of information within the enterprise, due to the simplicity of its search, processing and distribution.
The information infrastructure of a corporation may include the following information resources: hypertexts and hypermedia; office documents; graphic information; archive files; email messages; news; Database; application software. The direction and content of information flows depends on the nature of resources, the means of their creation, mechanisms and rights of access to information.
Electronic commerce (e-commerce) is becoming more widespread - a form of delivery of goods (services), in which the selection and ordering of goods is carried out through computer networks, and settlements between the buyer and supplier are carried out using electronic documents and (or) means of payment. At the same time, both individuals and organizations can act as buyers of goods or services.
E-commerce includes not only online purchase and sale transactions. The area covered by this concept also includes such activities as conducting marketing research, identifying partners, maintaining relationships with suppliers and consumers, organizing document management, etc. Thus, e-commerce is a complex concept and includes electronic data interchange as one of its components.
Thanks to the Internet, e-commerce has become accessible to companies of various sizes. A storefront on the WWW gives any company the opportunity to attract customers from all over the world. In real time, new sales channels are being formed - virtual, requiring minimal material investments. If information, services or products (for example, software) can be delivered via a computer network, then the entire sales process, including payment, can take place online.
The most developed e-commerce technology is EDI (electronic data interchange), which eliminates the need for processing, mailing and re-entering paper documents into computers, i.e. excludes a process that can generate errors.
The implementation of the e-commerce system is specific for each specific task. However, in each of its solutions there are common features: client-server technology; use of databases; the presence of scripts that process user actions.
The most common design solutions:
- electronic store;
- Digital catalogue.
To implement each of the projects, it is necessary to select the required software, hardware and technological solution. The software is divided into operating systems, web servers, database management systems, scripting languages.
For each e-commerce system, it is necessary to select its own hardware and software solution. So, for the "electronic store" system, a server with Unix OS, Apache web server, Oracle database management system, and Pentium 3 hardware must be required. Communication with the database must be carried out by cgi-scripts.
E-commerce opens up great opportunities for increasing the profits of enterprises. A broader concept is electronic business (e-Business), which includes, in addition to commercial activities, qualitatively new technologies that allow a company to achieve a competitive advantage by improving customer service and optimizing relationships with partners.
Business in modern conditions is operational management and high labor productivity with an ever-growing information load. In an evolving competitive environment, there is an increasing need for cost-effective and simple means of quickly accessing critical applications and information, sharing data and collaborating within a firm and/or business community. These needs are experienced by both company managers and business partners, potential and existing customers who interact with the company on technical and economic issues of supply, obtaining information about products. By enabling direct contact anytime, anywhere, the Internet enables businesses to build interactive relationships with customers and suppliers and deliver products (services) faster and at lower cost.
The essence of e-business is not limited to software and computers. The implementation of the idea of e-business requires a revision of the entire model of business turnover. Like traditional business, e-business requires an integrated approach, including planning and management, supported by technology, processes and structure. This requires secure and reliable software and hardware, networks, communication channels and, of course, the Internet.
The Internet has become a universal business environment that connects companies with each other and with the consumer audience. All companies, regardless of their size and age, have gained access to e-business.
E-business allows you to make the main business of the company more profitable, and the company - more competitive. This is carried out, first of all, due to the full automation of all business processes of the enterprise, from the purchase of the necessary materials to the distribution of finished goods.
It should also be specially noted that the basis for the development of the economic activity of enterprises and organizations is innovative activity and its basis is scientific and technical information. To ensure monitoring and search for scientific and technical information, Internet search engines are used, which are discussed in the next paragraph.
LickliderJ. C. R. Man-Computer Symbiosis // IRIE. Transactions on Human Ractors in Electronics, 1960, March. Vol. YFE-1. P. 4-11. URL: http:groups.osail.mit.edu/medg/people/psz/Licklider.htm/.GBPOU KK
"Krasnodar Assembly College"
LECTURE:
Modem. Units.
Internet technologies.
Teacher
information technologies
Nesmelova A.R.
Krasnodar2015
Modem. Units.
Internet technologies.
Explanatory note
This manual is intended to study theoretical knowledge on the topic “Modem. Units. Internet technologies." in the course of the discipline "Informatics and ICT" for the first years of technical specialties, focused on the implementation of the federal component of the state educational standard (hereinafter - GEF) of secondary (complete) general education in computer science at the basic level within the main educational program of secondary vocational education, taking into account the profile of the received vocational education.
The content of the main sections of the lecture:
Introduction
Modem
Units
History of the Internet
Offline technologies
Online technologies
Conclusion
Target: familiarization of students with the theoretical foundations of the creation and operation of the Internet, the disclosure of the basic concepts of the global network, the study of the features of various Internet technologies.
Tasks: give the concept of the Internet and study its capabilities, basic means and methods of organizing communication, compare the features of various Internet technologies, study the basic units of measurement of data transfer speed, learn how to calculate the amount of information transmitted
Introduction
The Internet is a worldwide system of computer networks that are interconnected and operate using data packet routing and protocols.IP. Based on the Internet, a global information space has been formed andWorldWideWeb(The World Wide Web). By the way, very often the Internet is also called the World Wide Web, but this is erroneous, since the "Internet" and "World Wide Web" mean completely different concepts. Also, on the basis of Internet technologies, many other data transfer protocols have been created. Without the Internet, the information development of society would not be as rapid and fruitful as it can be observed today. More than 1.5 billion people regularly use the Internet per day, although this figure is very approximate, because every day the number of network users is growing steadily.
Considering the principle of the Internet and, accordingly, answering the question of what the Internet is, it should be noted that its main components are government and home computer networks. To unite all these networks, the Internet protocol was invented (IP) and the principle of data packet routing.
The task of routers at the junction of networks, regardless of whether they are software or hardware, is to automatically sort and redirect data packets based onIP- the address of the recipient of the packet. Thanks to the protocolIP, a single address space is formed all over the world, however, its own subspace exists in each individual network. This address organization avoids conflicts between individual networks in a single world space, which allows data to be transmitted smoothly and accurately.
For communication between computers remote from each other, ordinary telephone networks can be used, which to one degree or another cover the territories of most states.Telecommunication - remote data transmission based on computer networks and modern technical means of communication. The only problem in this case is the conversion of digital (discrete) information, with which the computer operates, into analog (continuous).
Modem - a device connected to a personal computer and designed to send information (files) over a network (local, telephone). The modem converts analog information into discrete information and vice versa. The job of a modem modulator is to convert the bit stream from the computer into analog signals suitable for transmission over a telephone channel. The modem demodulator performs the inverse task. A fax modem is a device that combines modem capability and the means to exchange fax images with other fax modems and conventional telefax machines.
Thus, the data to be transmitted is converted into an analog signal by the "transmitting" computer's modem modulator. The receiving modem, located at the opposite end of the line, "listens" to the transmitted signal and converts it back to digital using a demodulator. After this work is done, the information can be transmitted to the receiving computer.
Both computers, as a rule, can simultaneously exchange information in both directions. This mode of operation is called full duplex.
Duplex mode of data transmission is a mode in which data is transmitted simultaneously in both directions.
Unlike duplex transmission mode,half duplex It implies transmission in only one direction at a time.
In addition to the actual modulation and demodulation of signals, modems can perform compression and decompression of the transmitted information, as well as search for and correct errors that have occurred during data transmission over communication lines.
Units. One of the main characteristics of a modem is the modulation speed, which determines the physical data transfer rate without taking into account error correction and data compression. The unit of this parameter is the number of bits per second (bps), called baud.
Bit per second (English Bits persecond, bps) - the basic unit of measurement of the information transfer rate used at the physical layer of the OSI or TCP / IP network model.
At higher levels of network models, as a rule, a larger unit is used - bytes per second (B / s or Bps, from English bytes per second) equal to 8 bits / s.
Unlike baud (baud; in binary coding, baud also denotes the number of bits per second), bits per second measures the effective amount of information, without taking into account the service bits (start/stop/parity) used in asynchronous transmission. In some cases (with synchronous binary transmission) the baud rate may be equal to the bits per second.
Any communication channel has a limited bandwidth (information transfer rate), this number is limited by the properties of the equipment and the line (cable) itself.
The amount of transmitted information is calculated by the formula Q=q*t, where q is the channel bandwidth (in bits per second), and t is the transmission time.
History of the Internet
The first mention of the Internet as a reliable information transmission system was made by the US Department of Defense in1957 year. The US military was concerned that America should have a system for transmitting military information if there was a war.
All developments were financed by the Ministry of Defense, and as a result, a network appearedARPANET. Over the yearsARPANETimproved, which led to its use in the scientific world, but for the first timeARPANETwas installed at the University of California, Los Angeles,1969 year, 2 September. Almost two months passed between the installation of the first server and its first launch. The second server of the network was installed at the Stanford Research Center, and the distance between the two servers was 640 kilometers.
At 9 o'clock in the evening,October 29, 1969 year, the first attempt was made to transfer data from the first server to the second. Of course, not everything went smoothly usingARPANET, in particular, the launch of the network failed the first time - scientists were able to send onlyLOGinstead ofLOGON(meaning "login"). After 1.5 hours, at 22:30 the second attempt was successful. This day can be called the birth date of the Internet.
IN1971 In the year the Americans proposed the first program, which became very popular - it was the first e-mail. In principle, even today the most popular among Internet users is e-mail, however, a modern user has the right to choose, since there are several programs on the network for sending e-mails.
IN1973 year the Internet becomes international, because it was in this year that Americans connected to their networkARPANETseveral foreign organizations located in Norway and Britain. The use of the network was mainly based on the forwarding of emails. But at the same time, in the 70s, the first bulletin boards and newsletters appeared. The active development of protocols was indicated by the end of the 70s, the beginning of the 80s, and already in 1983 protocolsIPhave been standardized. Initially, networkARPANETworked on protocolNCP, but thanks to Jon Postel and some other programmers,ARPANETswitched toTCP/ IP, which justified the hopes of its authors, because we use it today. Since 1983 the world has been talking about the networkARPANEThow about the internet.
The term "domain name system" came into use in 1984. At the same time,ARPANETgot the strongest opponent -NSFnet, a network founded by the US National Science Foundation.NSFnetis an extensive inter-university network with more opportunities thanARPANET. NetNSFnetwas able to connect 10,000 computers to itself in a year, which led to the renaming of the network to the Internet. After 4 years, Internet users were able to communicate live, that is, in a chat, thanks to the developed protocolInternetRelayChat.
The British scientist Tim Berners Lee can rightfully be called the "godfather" of the concept of the World Wide Web, since it was this person who proposed the World Wide Web in 1989 at the European Council for Nuclear Research. By 1991, Tim Berners Lee is developingURI, protocolHTTPAndHTML. A year earlier, in 1990, the first network ceased to exist, as competition fromNSFnetbecame forARPANETlosing. Since 1990, the Internet has been using a telephone line to connect.
After 20 years, many experts agree that the history of the Internet can be divided into two eras. The first was before the advent of the web browser.NCSAMosaic, which was introduced in 1993; the second - after the appearanceNCSAMosaic. Within a year, the browser allowed the Internet to spread around the world. Since 1995, the World Wide Web has been the main provider of information on the Internet, and by a significant margin, ahead of the file transfer protocol.FTP. The term "World Wide Web" firmly occupies a leading position in 1996, leaving behind the definition of "Internet".
Overview of the main Internet technologies
Internet technologies, as well as industrial or financial technologies, determine the means and form in which people work together to achieve certain goals.
Internet technologies combine information flows from a large number of actors to achieve greater consistency in their actions, as well as a more accurate definition of the content of their future actions. Internet technologies open up new broad horizons for improving communications and information exchange between people on a global scale.
These technologies can be divided into two main categories:
1) offline technologies - means of distributing messages that provide communications in off-line mode (i.e., allowing significant asynchrony in messaging);
2) online technologies of synchronous communications in real time (on-line).
Offline technologies
The most static representative of the first type are classic web pages that carry information (perhaps quite often updated) from the source to the consumer, but do not contain convenient means for two- or multilateral interaction between authors and users of information (in later modifications of the web page technology this shortcoming is gradually being eliminated).
A more dynamic representative of the first type of technology is teleconferences, or as they are also called "newsgroups" (newsgroups), and "mailing lists" close to them, which allow for several hours to distribute messages of individuals among a gigantic audience and give quite convenient opportunities for mass discussions and exchange of opinions.
Let's take a closer look at the three most used ways to implement asynchronous communications:
Mailing lists (mailing list) are the oldest representative of interactive Internet technologies. To participate in them, it is enough to have your own e-mail address and know the address of the desired mailing list. A letter is sent to this address, the text of which consists of some commands or a message for users of this mailing list. To get a list of commands, as a rule, it is enough to send a single-word help letter to the mailing list address. The header of emails with commands for the mailing list should usually be empty. If you sent a letter with a command to subscribe to this mailing list (most often this command is subscribe), then your address, which is taken from the service headers of your letter, is placed in the list of addresses to which all incoming messages will be duplicated, except for letters with commands.
Newsgroups (newsgroups), in Russia they are more often called teleconferences, are technically more advanced than mailing lists and therefore often include the capabilities of the latter.The main difference between newsgroups and mailing lists is that the user may not receive them on his computer by e-mail, but can view them directly on the so-called news servers (newsserver). This requires special software. Browsing different newsgroups becomes easier and faster than mailing lists. From a technical point of view, newsgroups exist due to the fact that all the world's news servers exchange messages from their users on overlapping lists of newsgroups. Different servers may store different sets of newsgroups for their users and for different durations. For example, the Infoteka news server stores about 1500 newsgroups, and the similar NSU server does not have several hundred groups more. For different groups, the period for storing messages can vary from one day (group "test" in NSU) to several months.
Web forums (web forums)are the next stage in the development of the technologies described above and represent the integration of the capabilities of mailing lists, newsgroups with web pages. As a result, familiar web pages, which are superior to other technologies in terms of expressiveness, receive additionally quite powerful interactive properties.
Online technologies
The second type of technologies that provide synchronous exchange of information in real time include the so-called "talk channels" (chat channels), as well as still little used audio and video conferences. It is estimated that about a third of the time users spend on the Internet is spent on "cyber conversations" carried out using "talk channels". The growing popularity of this technology of "live" communications is explained by its simplicity (the user receives on the screen of his computer the texts of replicas from all participants in the cyber-conversation and can immediately enter his own text, which takes its place in the sequence of replicas of this conversation), a variety of expressive means (except for texts, in the same way, pictures, audio and video clips, etc. can be embedded in the "conversation", as well as the possible anonymity of the interlocutors, which gives such "conversations" liveliness and immediacy. The number of conversational channels is estimated at several thousand, many of which operate around the clock.
Cloud computing is a distributed data processing technology in which computer resources and capacities are provided to the user as an Internet service.
Spline offices are applications implemented using the innovative Internet technology "software as a service" (English, Software as a Service - SaaS), in which the software is created and maintained as a web application on the developer's server, providing users with access to programs through the Internet. Microsoft Office 365 can serve as examples of such offices. Another “Google Docs cloud technology, its functions: creating office documents in the form of text, tables, presentations and dialog forms, providing up to 1 gigabyte of memory with the ability to create a hierarchy of folders and collections for storage files, export-import of documents in known formats (DOC, XLS, ODT, ODS, RTF, CSV, PPT, including MS Office 2007/2010 formats). the ability to save an office document in an HTML version for publication on the Internet, preview and print the document.
However, if the Internet and networks become more accessible, then Internet technologies are complex systems that combine both physical and logical components.
Physical components have a material value, which allows you to develop an Internet technology business.
The physical elements of Internet technology include:
Network technologies. Servers. data centers;
Internet software;
Topology of the Internet (interaction of computers and servers in the network);
Network services (e-mail, DNS service, FTP protocol, etc.);
Local and home networks, routers.
Logical components allow you to create almost any Internet resource on the network: a website, a web application, a web portal.
Web technologies:
Markup languages (HTML);
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS);
Scripting language (JavaScript);
Browsers;
Web pages DOM (Document Object Model (DOM);
markup languageXML (Extensible Markup Language);
Search engines;
SEO(search engine optimization).
The division into physical and logical components is somewhat arbitrary, because they can only exist in interconnection and do not have a special purpose without each other.
You also need to understand that this is, of course, an incomplete list of Internet technology elements. But it gives a general idea of such a voluminous concept as the Internet technology.
Conclusion.
At present, the Internet is developing exponentially: every one and a half to two years, its main quantitative indicators are doubling. This applies to the number of users, the number of connected computers, the amount of information and traffic, the amount of information resources.
The Internet is developing and qualitatively. The boundaries of its application in human life are constantly expanding, completely new types of network services and telecommunication technologies are emerging.
The life of modern society is becoming more and more computerized. The requirements for the efficiency and reliability of information services are growing. Scientists are developing fundamentally new forms of global networks.
Bibliography
1. Ugrinovich N.D. Informatics and information technologies. Textbook 10–11 cells. - M., 2010.
2. Ugrinovich N.D. Teaching the course "Informatics and ICT" grades 7-11. - M., 2010.
3. Beshenkov S.A., Kuzmina N.V., Rakitina E.A. Computer science. Textbook 11 cells. - M., 2009.
4. Beshenkov S.A., Rakitina E.A. Computer science. Textbook 10 cells. - M., 2009.
5. Maksimov N.V. Partyka T.P. Popov I.I. Modern information technologies - M: Forum, 2012
6. Mikheeva E.V. Titova O.I. Computer science. - M. Academy, 2012.
7. Guseva A. "All about the internet", M, 2008
8. WikiKnowledge: hypertext electronic encyclopedia
9. http :// www . wikiknowledge . en
10. Wikipedia: free multilingual encyclopedia http://ru.wikipedia.org
11. Newspaper "Informatics
12. Internet - a collaborative learning environment
13. Institute of New Technologies
14. Collection of digital educational resources
 Why choose Vimeo over YouTube as your video host
Why choose Vimeo over YouTube as your video host Creating a photo in Skype How to set your photo as an avatar in Skype
Creating a photo in Skype How to set your photo as an avatar in Skype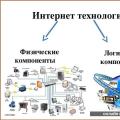 Possibilities of modern Internet technologies
Possibilities of modern Internet technologies