Data compression H 264 audio data. Profiles codec H.264
Compression type H.264, more famous called MPEG-4 Part 10 Advanced Video Codec, quickly became the prevailing standard for video compression for the television industry.
The fourth generation of codecs, H.264 becomes popular even among the content for leading mobile devices. Manufacturers install codec support in almost all devices. Such universality involves the use of the codec everywhere. But the same quality makes the codec much more difficult in the settings for optimal use than its predecessors. It requires higher technological capacities for encoding and decoding processes, which limits its use in low price categories.
This is one of the topics that numerous discussions are being conducted on the introduction of H.264 into all phases of television production and how quickly needs to be adapted to the streaming media impairment to completely change its digital entity.
What is H.264?
H.264 / MPEG-4 Part10 AVC - advanced, today, compression technology - Command team performance known as Joint Video Team (JVT). The group was founded by ITU members (International Telecommunication Union) and (MPEG) Motion Picture Expert Group and published its first technical document - the ITU-T H.264 and ISO / IES MPEG-4 Part 10 specification in 2003. At the same time, a team of specialists assured that the codec will be adopted and adopted in the production of telecommunications and television industry already soon.
The MPEG-4 specification defines 27 separate and frequently compatible standards called parts (part) that can be applied in television. But some of them are not compatible and have nothing to do with Part 10. Only H.264 equivalent to MPEG4 Part10 specification. To avoid confusion, you should adhere to only these concepts in the selection of equipment for production.
H.264, in turn, also has many subsections, called profiles, each of which has its own specific qualities and limits of applications. Some of them are crowded with more modern profiles. Specifications change as often as profiles are replaced.
The broadcasters are most interesting to Constrained Baseline Profile, which is used for Internet broadcasting and broadcasting for mobile devices since 2009. For television terrestrial broadcast, Main Profile is used. Scalable High and Scalable High-Intra profile that was highlighted from High's profile in 2007 is used in the video production and in some broadband networks. Also H.264 was standardized for 3D video starting with the 11th version, given its possible application in the future in 3D television.
H.264 Inherited from its previous three generations of codecs The main directions in the coding techniques, but with a more developed mathematical apparatus and with respectual advantages.
- Frames of digital video are analyzed, compared with previous and subsequent frames, identity and differences are detected. As a result, the image of the playable frame is predicted and in the last step, if the data is lost, they are restored from previous data.
- The choice of various coding algorithms for optimal miscalculation of processes and control over their diversity - the feature of the codec. This is important to optimize coding for narrow bandwidth and limited resolution devices.
Advantages H.264.
The codec has several advantages, namely:
- Low Bit Rate at a high level of quality. This is especially important for cable, satellite, and in Ukraine it is especially important for essential, operators. Instead of a single channel with MPEG2 coding, you can accommodate two with encoding H.264. This significantly reduces the cost of broadcasting and makes it possible to broadcast in an acceptable quality where data transmission technologies are limited in the bandwidth.
- Acceptable quality Image with low Bit Rate. This quality can be used in limited bandwidth, for example for mobile devices. In many cases, MPEG-4 is the only possible standard for broadcasting at low Bit Rate.
- Less technologies on the market - more audience. If you would like to add a new form of broadcasting, then the chances are only in coding technologies based on H.264. Solutions using MPEG-4 support and infrastructures supporting MPEG-4 will be much cheaper than using some unusual devices.
- The best compatibility for a long time. The choice of H.264 support devices is constantly expanding, and in the near future each media device will have a built-in H.264 codec. And so it will continue until this compression method changes another. But he should be so revolutionary that many years will go to his creation.
- Low cost of introduction. Low competition from the remaining standards will lead to a rapid growth of the market and decrease in products prices, we can also observe a gradual decline in demand for expensive multi-standard devices. Production of devices combining the encoder and player will grow.
Optimization H.264 for television
The flexibility come and complexity. And H.264 is no exception. Installations of the H.264 encoder for your solution may be simple if you select them by pressing one default button. In fact, the optimal configuration of the encoder is very complex. Only one popular H.264 codec settings library has more than 200 configurations.
Fortunately, the most common sets are available in templates, however, the best features of video playback can be selected only by careful customization in the user interface.
There are several critical points that are especially important for H.264.
— Permanent (CBR) and variable (VBR) Bit Rate. With constant Bit Rate, and approximately half of the traffic has a CBR, there are no questions regarding complexity or other factors that would expand the bandwidth. This is very good quality for threads for mobile devices, because they have a narrow bandwidth and not a very powerful processor, which is easier to handle a constant data flow without peak loads. CBR is also convenient to use in Internet broadcasting using adaptive streaming. Because the player automatically switches back and forth between different threads. And the CBR helps the player to synchronize and play video seamlessly and stable.
But the CBR is not optimal from the quality of the quality, because the flow does not change depending on the dynamics and complexity of the video. While the specifics of the VBR allows you to raise Bit Rate in the necessary complex places and reduce the compression ratio to obtain a better image. This is necessary in scenes with the rapid movement of small items. On the other hand, more bits - wider bandwidth. It can create big problems. Therefore, if you need a high-quality H.264, download the movie in advance.
- Dimensions of macroblock. Like other Codecs H.264 creates individual distributions in the captured frame, called macroblocks. Video compression and compensation technology, which creates the magical compression of each macroblock, ultimately predicts a frame calculated from the difference between the final and initial macroblocks. The old codecs had a fixed magnitude of macroblock 16x16 pixels, but H.264 allows you to choose this size. Despite the fact that the minimum block size is 4x4 pixels, in special cases blocks can decrease to 1 pixel, that is, not compressed.
Small, medium and large blocks, alternating in frames, adaptively regulate the coding process, contributing to the optimal image and significantly determining the load of the processor during the Real-Time coding. For encoding in broadcast solutions, it is preferable to use minimal macroblocks, but so much so that it would not be possible to cause frames or other delays associated with the compressor behind. An increase in the size of macroblocks can be achieved, if necessary, by pre-filtering the image (for example, BBS). The main thing to determine the compromise of these parameters.
Most professional coders have the ability to automatically change the macroblock size when changing the size of the output frame.
-Gop structure. Group of Picture (GOP) usually changes as often as required to insert a full frame, to play predicted frames without significant losses. Your selection of settings can significantly affect the coding process. Most encoders have an automatic ability to insert a full frame in the scene on time. However, some content, for example, as news, has frequent scenes shifts, and a frequent automatic full frame insert can lead to large delays. I remember one such device that did not start if there was no first full frame in a new feet. Well, it is from a row, but an increase in the GOP structure due to full frames can create an additional flow delay by 1-2 seconds. If the cache device is overflowed, the audience will start annoying the stop-frames and scattering the video.
Thus, using some codec settings, you can adapt the image for specific tasks.
P.S. I would not feed the big illusions about the quality of broadcasting DVB-T2 in Ukraine. The used profile with a 8-bit transformation will not allow, even with the most optimal solutions, lift the clarity of the TVL above 400. That is, the clarity will remain at the same level as now. And the size of the screens in households in recent years has doubled. Yes, of course, essential interference and noises in the zones of weak and unsure reception. But natural distortions introduced by coding with a flow rate of only 2.5 MBS. The output is one - very gently filter high frequencies, increasing the size of macroblocks, but without fanaticism. How to do this in a separate television company C, as a rule, unpredictable content is a separate headache of the main engineers.
Today, TV companies have freedom of choice regarding compression of television sign. MPEG-2 formats, H.264 and JPEG2000 are the most competitive options for compressing the video stream at a professional level. Ultimately, the network infrastructure, bandwidth and budget are decisive factors for the television company that help to decide on the "right" choice. MPEG-2 and H.264 formats are effective compression solutions of multimedia applications for the purpose of their subsequent playback.  Experimental arguments can be given in favor of the JPEG2000 format, which is based on advanced intraframe coding methods and provides a high degree of flexibility and controllability, not comparable to the flexibility and controllability of other compression formats. Moreover, the fact of the appearance of increasing and large varieties of transmitted video applications that require a lower delay time and higher image quality, makes the JPEG2000 format with an optimal solution to satisfy the video transmission requirements in HD quality.
Experimental arguments can be given in favor of the JPEG2000 format, which is based on advanced intraframe coding methods and provides a high degree of flexibility and controllability, not comparable to the flexibility and controllability of other compression formats. Moreover, the fact of the appearance of increasing and large varieties of transmitted video applications that require a lower delay time and higher image quality, makes the JPEG2000 format with an optimal solution to satisfy the video transmission requirements in HD quality.
The main task of all television companies is, regardless of the infrastructure of the network, the selected compression method and features of broadcast applications - is the transmission of the maximum quality signal at a given bandwidth, while limiting costs in order to obtain maximum profits. Keep in mind that the transmission of the video stream is a complex circuit of processes. A process occurred inside the chain affects the process of transmission of the video as a whole, as a result, serious flaws inside the chain affects all subsequent links and leads to a deterioration in the quality of video transmission in general. Of course, the way that the selected compression format is implemented, and how it is managed by it, also plays an extremely important role in achieving the best performance regardless of the selected compression scheme.
MPEG-2: "Outdated" codec
Video compression algorithms such as MPEG-2 and H.264 are codecs that are based on a discrete cosine transformation (DCP). In order to reduce the data of the video signal between the frames of the frames, these codecs use an intercader prediction algorithm. The essence of this algorithm consists in the method of differentiated coding, when the subsequent frame is compared with the original, after which the coding is coding only those pixels that have changed.
As a result, the number of pixels that must be encoded and transmitted is reduced. When such a coded sequence is transmitted to the TV screen, the received video is no different from the source sequence of frames.
The appearance of MPEG-2 was due to the need to broadcast signals at a higher data transmission rate - SD-format signals (bit rate value from 3 MB / s to 15 MB / s) and HD-format (bit rate from 15 MB / s to 30 MB / from). When transmitting a video using the MPEG-2 predicative compression method, each encoded frame in the image sequence can be transmitted as an independently compressed frame ("I-frame"), a compressed frame using motion prediction in one direction ("P-frame") and a compressed frame Using motion prediction in two directions ("B-frame"). Due to the reduction in the spatial and temporary redundancy of MPEG-2 provides increased compression. Nevertheless, the use of "B-frames" leads to the appearance of a delay in the alert, which depends on the number of "B-frames" transmitted. With a large number of "B-frames" transmitted, this delay can be very significant.
MPEG-2 is still a widespread codec and is considered as a competitive selection due to its low cost of introduction and support of a wide range of color rendering - 4: 2: 2. Nevertheless, there are a number of restrictions, which are due to the codec themselves and standards that regulate its implementation.
For example, MPEG-2 compared with competing codecs requires, as a rule, higher bandwidth to ensure sufficiently high quality video. Due to the streaming bit structure of the signal and its transfer form in the form of separate packets, the encoded signal in MPEG-2 is extremely sensitive to errors and any loss of information. The loss or damage of one of the packages has a significant impact on the decoding process, which leads to "broken" frames or expressed image distortions, and this will ultimately lead to the termination of the use of MPEG-2 in the professional television environment.
H.264: Next Generation codec
H.264 or MPEG-4 Part 10 (Advanced Video Coding) The codec was developed as an alternative to MPEG-2 codec and is characterized by increased performance and a wider set of tools, which ensures high flexibility regarding information transmission. As a result of H.264, compared to MPEG-2, provides equivalent video quality at a lower data transfer rate. When switching to H.264 encoding, compared to MPEG-2, the bandwidth sufficient to transmit the image of the same quality can be reduced by up to 50 percent. This codec uses asymmetric architecture. The complexity of calculations is minimized in it, which causes its high flexibility sufficient to apply this codec to a wide range of applications, including broadcast, storage and transfer of data on wireless multimedia communication.
H.264 compression algorithm is similar to the MPEG-2 algorithm and is based on the same basic principles, including compensation of motion with variable block size and discrete cosine transformation. Moreover, H.264 is characterized by high performance and reliability. It performs both spatial prediction in intraframe coding, and an estimate of the movement during intercader coding, which improves compression efficiency. When intraframe coding, each frame is encoded by itself, without the use of information of neighboring frames. In addition, H.264 uses pre-processing of steps, using neighboring pixels from previously encoded blocks for this, which is an advantage compared to the intrafoon spatial correlation.
The key features of this standard are the efficiency of compression and data transfer, as well as the focus on the compression of a wide range of applications. Due to the fact that today the codec maintains 17 profiles and 16 levels, each of which is aimed at a specific class of popular transmitted video applications, a high level of flexibility and scalability is achieved.
H.264 format is characterized by the same limitations as for MPEG-2 format. Ultimately, these restrictions are associated with the possibility of existing technology, which prevents the use of H.264 format in a professional broadcast environment. To date, the most technologically advanced codec compatible with broadcasting standards is H.264, which performs a video compression at a speed of 80 MB / s, limited by a resolution of 8 bits. The network implementation based on H.264 may be expensive. The cost compared to competing standards can be four times higher due to cost and power consumption. Thanks to the architectural asymmetry of codecs, the impression may be the impression that high-quality decoders have low costs, with the result that users are very often surprised by a high price for professional video discoders.
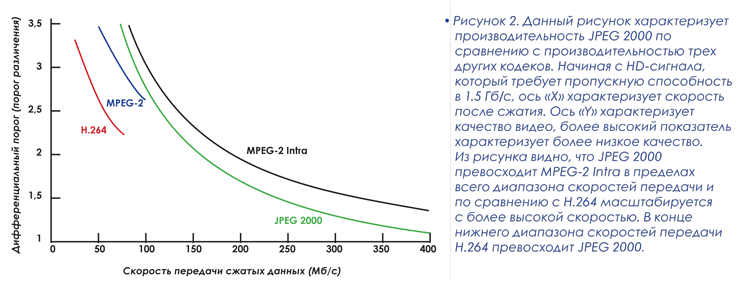
JPEG2000: choice of progressive compression method
The JPEG2000 method offered by the modern market is its key advantage. The standard and coding system JPEG2000 are based on the "Wavelet-Technology" image compression. Initially, it was conceived not as a codec for compressing video, but as a codec compression of graphic images. The intrafoon coding scheme applied in it has a number of advantages characteristic of the entire cycle of broadcasting - delivery, formation, as well as primary and secondary distribution.
JPEG2000, compared with H.264 and MPEG-2 formats, well known for its excellent visual quality (see Figure 1). JPEG2000 performs encoding within the full frame, while other compression schemes require the image to be broken into smaller blocks, as a result of which the deterioration of the quality occurs unevenly and may differ within the frame. This leads to the appearance of visually annoying distortion, known as the "blocking effect". In the case of JPEG2000, the loss of quality occurs evenly throughout the region of the frame and is visually perceived as the smoothing of the edges, in other words, there is a blur. Such a distortion is visually less annoying than the "blocking effect", since the blur to a greater extent corresponds to the natural perception of the human eye. JPEG2000 has the unique opportunity to deliver information in the original form for subsequent processing. By providing high quality at a lower level, high quality transmission to a higher level is possible. The JPEG2000 video remains practically intact when the coding / decoding multiple cycles is implemented. This allows you to save high quality video, passing it on this chain.  JPEG2000 is characterized by a low delay time - about 1.5 frame or less on the entire coding-decoding cycle. This parameter is critical for interactive applications and can lead to a lack of communication when moving from one frame to the next frame. Low delay time of the order of 45 ms in the compression of the HD-flow is an advantage compared to H.264 and MPEG-2 formats, the delay time in which reaches from one to two seconds.
JPEG2000 is characterized by a low delay time - about 1.5 frame or less on the entire coding-decoding cycle. This parameter is critical for interactive applications and can lead to a lack of communication when moving from one frame to the next frame. Low delay time of the order of 45 ms in the compression of the HD-flow is an advantage compared to H.264 and MPEG-2 formats, the delay time in which reaches from one to two seconds.
High transmission rate, which is achieved through JPEG2000 compression is also critical. When comparing implemented projects, it is noted that, as a rule, JPEG2000 can operate at very high speeds - much higher than H.264. To transmit high quality images, this is a key point, since the bandwidth can be limited to a specific type of infrastructure, but the bandwidth width is not necessarily critical. For example, HD video at 1.5 GB / s cannot be transferred via an Ethernet network to 1 Gbps, but for this purpose the entire channel can be highlighted. Therefore, the HD video transmission can be carried out if you use the entire bandwidth and apply a "light" JPEG2000 compression to achieve both the highest quality and fitting into the width of the channel or, when it is appropriate, encoded using mathematical compression without loss with a view to Exceptions of loss of video information.
One of the most significant advantages of the JPEG2000 format is its flexibility. Possible data transfer by multiple network infrastructure types - Ethernet / IP, SONET / SDH / PDH and fiber. When the data is packed with JPEG2000 in ASI-thread, the video can be transmitted everywhere, at any time and at any distance. JPEG2000 performs independent coding of each field and each frame, brightness and color component. The quality that is achieved at the expense of mathematical compression without loss is comparable to the quality of mathematical compression with losses. The video can be encoded by mathematical compression without loss, but because of the insufficient bandwidth of the channel can be cut and convert into compression with losses.
Structurally for JPEG2000 is characteristic of the same level of complexity both for the coding process and for the decoding process. Since JPEG2000 is a symmetric codec, the same hardware can be provided as an encoder and as a decoder, while asymmetric codecs require completely different hardware, especially at high data transfer rates. The relatively low complexity of JPEG2000 has advantages in the cost, capital and operating costs, and also reduces network power costs.
Let's sum up
Each of the codecs discussed in the article plays its individual role in the field of high-quality data transfer. H.264 / MPEG-4 and MPEG-2 codecs are still relevant in the field of professional television broadcasting. They provide high quality in low-capacity networks, but they are not necessarily the only right choice in all possible applications.
JPEG2000 provides high image quality and low delay time when encoding in several cycles. To date, he confirmed its significance in all areas of video technology, in the field of data on IP and 3G networks, as well as in HD and 3D technologies.
In addition to the quality and infrastructure of the network, in the process of comparison and the choice of the compression method, it is necessary to take into account the degree of resource costs and its cost. In general, MPEG-2 and H.264 compression methods are expensive, energy-intensive and require the use of complex technologies.
Since the JPEG2000 codec compared to others requires less energy consumption and generally provides greater scalability, flexibility and image quality, then it opens a brilliant future. An increasing number of worldwide broadcast service providers, as well as television companies use JPEG2000 to broadcast large, globally significant events - especially using IP network capacities. However, the existing situation is constantly changing, and possibly, tomorrow we will appear to the new, more "tricky" method of compression.
Today, observation cameras can be seen almost every step. You may also plan to install one or more cameras at home. Such devices operate with video files of Formats. 64 or H.264. But how to watch the video and how to open the file will consider in the article.
Differences and similarities of Formats 264 and H.264
Format.264. - These are untreated elementary threads of H.264-ES video files (also called the MPEG-4 temporary video file). In turn, H.264-ES is part of the H.264 format specification. Old DVR models write video in format.264. Such video files cannot be used for direct viewing by conventional players and require processing by special programs.
Allows you to reduce the video to the minimum size. After the video are full compression, video quality and audio still remains at a high level. This format has video surveillance cameras and new sample video recorders. H.264 files are also called MPEG-4 Part 10 AVC / H.264. Despite the long and terrible name on the network it is very easy to find the H.264 file player.
To open such files, you must use one of the following methods:
- use special programs and utilities;
- perform a video file conversion.
Opening video H.264.
Almost all popular programs and converters work with H.264 format, are popular:
Work with format.264.
Let's consider in more detail than to open the File.264 from the DVR or Observation Camera.
Special programs
For opening video.264, the following programs will be useful:
Video Files.264 You can combine or disconnect. How to do this we will look further.
Utilities
To play File.264, you must put it in a container format that can recognize any media player. For this purpose, we recommend using one of the following utilities:
- Demuxer - Can create DSM or MPC records. It is worth noting that the DSM files can only be played in this utility.
- Mkvcleaver - With it, you can cut video V.MKV.
- MKVMERGE - can change, cut, combine or disconnect video files. After processing video, the quality of the video does not deteriorate, and the format is changing N.MKV.
- Haali Muxer - can help in conversion, combining or disconnecting video files. After processing the video, it is assigned format.mkv.
 State Services Personal Account
State Services Personal Account State Supervisory Cabinet- Entrance on SNILS and Telephone
State Supervisory Cabinet- Entrance on SNILS and Telephone Single telephone rescue service in the Russian Federation
Single telephone rescue service in the Russian Federation